AI increases chances of lung nodules detection on chest X-rays: study
by
John R. Fischer, Senior Reporter | February 08, 2023
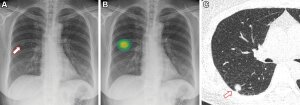
AI increases the chances of lung nodules being detected on chest X-rays.
With artificial intelligence, radiologists are more likely to identify actionable lung nodules on X-ray scans that require follow-up.
Researchers in South Korea made this assessment after applying AI in clinical practice to a group of 5,238 patients, comparing their results to a group of the same number with chest X-rays that were not examined with AI.
Lung nodules were identified in 2% of cases, with the detection rate for the AI group, 0.59%. The group without AI had a rate of 0.25%. In addition to lung nodules, AI can identify various abnormalities on chest radiography, which may be used to generate reports.
"Some of these findings may be used to triage patients who need urgent management. Deep learning techniques on chest radiography can also be used to optimize candidate selection for lung cancer CT screening and to predict survival in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease," Dr. Jin Mo Goo, from the department of radiology at Seoul National University Hospital in Korea, told HCB News.
Solid nodules with diameters larger than eight millimeters and subsolid nodules with a solid portion larger than six millimeters were considered to be actionable, meaning that they required follow-up according to lung cancer screening criteria.
The average age for patients was 59, and 11% were current or former smokers. All underwent chest X-rays between June 2020 and December 2021, and each indicated their age, sex, smoking status and past history of lung cancer.
Older age and a history of lung cancer or tuberculosis were linked to positive findings, but did not, along with other health traits, deter or heighten the efficacy of the AI, indicating that the technology may work consistently across different populations, regardless of whether they have diseased or postoperative lungs. No differences were found in false-referral rates between AI and non-AI interpreted groups.
Goo says this will contribute to identifying chest diseases, especially lung cancer, more effectively at earlier stages, and that AI could play a bigger role in helping radiologists facing high volumes of care.
The researchers are planning a follow-up study using chest CT to identify clinical outcomes and workflow efficiency.
The findings were published in the journal, Radiology.
|
|
|
You Must Be Logged In To Post A Comment
|
