Faster, safer, better: The latest in CT technology
October 12, 2020
by Lisa Chamoff, Contributing Reporter
Artificial intelligence has continued to infuse the CT market and is now being used by many companies to enhance image quality while keeping radiation dose as low as possible.
At the same time, with CT playing a large role in COVID-19 diagnosis, manufacturers have responded with tailored solutions and infection control protocols designed to ensure patients are as safe as possible.
Here’s a look at the latest CT products from several manufacturers.
Canon Medical
Canon Medical Systems USA received FDA clearance in the middle of last year for its Advanced intelligent Clear-IQ Engine (AiCE), which uses deep learning reconstruction to deliver sharp, clear and distinct images, according to the company. At the time, the technology was available for Canon Medical’s Aquilion ONE / GENESIS Edition wide-area CT, and the Aquilion Precision ultra-high-definition platforms. It has since expanded access across the majority of its portfolio, including the company’s new Aquilion ONE / PRISM Edition spectral CT, FDA-cleared early this year.
“Innovation flow-down across the portfolio this quickly is unprecedented,” said Dhruv Mehta, leader of strategic development for Canon Medical.
The new Aquilion ONE / PRISM Edition also includes Deep Learning Spectral capabilities that Mehta said “help reveal spectral insights without traditional trade-offs.”
“It’s positioned to make spectral imaging routine,” Mehta said.
The company also partnered with Surfacide to offer a UV-C disinfection unit for their CT scanners that Mehta said significantly brings disinfection turnaround times down in the era of COVID-19.
In July, the company introduced a new configuration of the Aquilion ONE / GENESIS Edition wide-area CT called the Aquilion ONE / GENESIS SP for cardiovascular imaging.
“Cardiac is one of most challenging imaging exams to perform,” Mehta said. “Within a single beat of your heart, it’s able to complete an entire acquisition.”
Curvebeam
Since December of last year, Curvebeam has been working on the HiRise, a weight-bearing CT imaging system that can scan the hips and pelvis in a standing position.
“Looking at hip alignment in three dimensions could significantly influence our understanding of the anatomy and how conditions like arthritis develop,” said Vinti Singh, director of marketing for Curvebeam.
Similar to the LineUP scanner, used for the knees and lower extremities, the HiRise is small enough to fit in a doctor’s office and can plug in to a regular wall outlet, negating the need to go to the hospital for a scan.
“COVID-19 has shown us we want to rethink hospital visits,” Singh said.
The HiRise is in use for research at the University of Iowa and the company is anticipating FDA approval in the fourth quarter of this year. Last year, Curvebeam had intended to simply modify its existing LineUP to scan up to the hip, but decided to release a completely new, third-generation system.
The gantry, with a 50-centimeter bore and 40-centimeter field of view, can flip 90 degrees, so the scanner can also be used for standing upper extremity scans, as well as supine foot, ankle knee and hip scans for standing and non-weight-bearing comparisons.
The company is also in the process of developing CubeVue Autometrics, an AI platform that can automatically segment foot and ankle data sets and run measurements in a matter of minutes.
“The foot and ankle are one of the most complex regions of anatomy, with 26 bones and 28 joints,” Singh said. “It’s like a very complex puzzle. Identifying each of bones manually can take up to a day per foot.”
The company is hoping for a release of the cloud-based software by the end of the year.
FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc.
FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc. recently completed development of the latest version 1.4 for its Persona CT system software, which includes more clinical features.
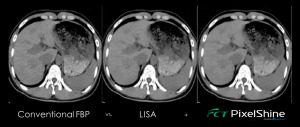
The company also released FCT PixelShine, a deep learning application that improves the image quality through denoising of low-dose CT images on any scanner.
“The new release of PixelShine is designed to find the best possible noise balance for the clinician,” said Rick Banner, senior director of marketing for FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc.
There are also FDA 510(k) pending updates to the company’s metal artifact reduction technology.
“Depending on the body region and type of metal, we can adjust the algorithm and make the image as beautiful and clear as possible,” Banner said.
There’s also an extended field of view, with an 85-centimeter bore and 60-plus centimeters of Hounsfield uniformity that’s FDA pending. Fujifilm believes this feature, once FDA approved and available to the market, will be crucial for oncology treatment planning.
GE Healthcare
GE Healthcare responded to the COVID-19 pandemic with a unique new solution called CT in a Box, which is a traditional scanner enclosed in a container and operated via remote control. This allows the technologist to perform the scan without entering the room. The scanner can be installed in two to three days, versus two to three weeks for a full hospital installation. It’s also easier to clean than a typical room and offers greater separation between patients and hospital staff.
The solution was developed in February, 2020 by the company’s China engineering team, with production starting in just 15 days, with the first system fully installed in Wuhan, China. The product has since been installed in more than 20 countries around the world.
“There was a desire for COVID-19 patients’ scanning to be done out of the hospital,” said Saad Sirohey, general manager for global CT digital and clinical applications for GE Healthcare.
At last year’s RSNA, GE Healthcare unveiled Revolution Maxima, part of the GE Revolution family of CT scanners. The Revolution Maxima includes a variety of applications and services designed to help simplify the CT workflow, including its new AI-based Auto Positioning solution. The solution, which generates a 3D model of the patient’s body and utilizes a deep learning algorithm to pinpoint the center of the scan range and automatically align it with the isocenter of the bore, is designed to also help avoid dose and image noise increases due to mispositioning.
At RSNA the company also displayed its Revolution EVO Gen 3, which includes TrueFidelity CT Images, GE Healthcare’s deep learning image reconstruction technology, available through the company’s Smart Subscription service.
Also through the Smart Subscription service are three new applications. The first, called Intelligent Protocoling, uses information from the patient’s exam order history and a facility’s practice to suggest the best protocol for each patient exam. The Hepatic VCAR application utilizes deep learning to automate liver and hepatic artery segmentation. And FastStroke automatically loads and processes CT studies and sends the processed images in an email format, speeding up CT stroke evaluations. The new version of FastStroke is pending FDA clearance.
Hitachi
At the end of last year, Hitachi received FDA clearance for its SCENARIA View 128-slice CT scanner.
The scanner is designed with bariatric imaging in mind, with an 80-centimeter aperture, a high-powered generator and a bariatric table that can shift left and right.
“It allows positioning to be easier and more accurate,” said Mark Silverman, director of CT Marketing for Hitachi.
The company also received FDA 510(k) clearance for Intelli IPV iterative reconstruction capability, which provides up to 83% dose reduction with the same image quality, according to Silverman.
Also new is Hitachi's SynergyDrive workflow automation, designed to reduce the number of keystrokes and clicks and allow for exam quality repeatability by automatically recognizing anatomy.
Hitachi’s new Comprehensive Ascent Program (CAP) is designed to simplify lowest cost of CT service, with one monthly payment that allows customers to lease equipment with service, X-ray tube replacement and unlimited onsite applications training included.
“We’re finding a lot of customers very interested to take advantage of that,” Silverman said.
NeuroLogica
NeuroLogica partnered with a surgical equipment manufacturer, Black Forest Medical, to create a radiolucent, carbon fiber skull clamp for interoperative use with NeuroLogica’s OmniTom CT. Previous clamps were made of metal, causing image artifacts during the CT scan, and in many cases making the CT dataset inadequate for the planned procedure.
“We are excited to partner with Black Forest Medical to bring advanced technologies, and more tightly integrated workflows to our clinical users,” said David Webster, chief operating officer of NeuroLogica.
The company also partnered with an emergency vehicle manufacturer to release an updated mobile stroke unit outfitted with an OmniTom CT scanner, which allows first responders to take immediate action in treating possible stroke patients by administering the necessary medicine or triaging them to the appropriate point of care, Webster said.
Previously, ambulances were equipped with the company’s CereTom scanner. The OmniTom provides better image quality and faster scan time, according to Webster.
Planmed
In the last 24 months, Planmed has introduced an ultra-low dose imaging capability for the Planmed Verity, a versatile cone beam CT (CBCT) imaging system that can be used in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing mode for point-of-care extremity imaging, that was released in 2012.
The technology maintains the resolution but cuts the patient dose by more than 75% as compared to the standard dose, said Steve O’Neil, North American sales manager for Planmed.
In mid-2019, the company released a new feature called CALM, a reconstruction algorithm that recognizes and corrects for minor patient movement during a scan.
Both features, the ultra-low dose imaging capability and CALM, are available as software upgrades for the company’s installed base of scanners.
Later this year, Planmed will be releasing two upgrades to the Verity platform, including an extended field of view to expand from 16 to 20 centimeters an automated stitching capability to combine up to three scans to achieve a much larger scan area than is possible with a single scan.
The company also recently signed a global distribution contract for an automated 3D analysis and treatment planning software for foot and ankle surgery from a company called Disior. The software can be used with the Verity as well as any other CBCT scanner.
Siemens Healthineers
Recently, Siemens Healthineers responded to the coronavirus pandemic by releasing its new CT Pulmonary Density AI algorithms. This workflow automation tool, which helps characterize and quantify abnormalities in the lungs of patients exhibiting COVID-19 symptoms, is part of the company’s AI-Rad Companion Chest CT software assistant.
The algorithms can be used to assess the severity and progression of COVID-19 by automatically identifying and quantifying abnormal patterns in the lungs said Peter Shen, vice president of Innovation and Digital Business at Siemens Healthineers.
“The algorithms provide several different complementary measurements, looking at ground glass opacities and consolidations, along with high-opacity abnormalities across the lung lobes that correlate to severe COVID-19 symptoms,” Shen said.
The algorithms have been trained on CT scans of COVID-specific patients from around the globe.
Just before last year’s RSNA, Siemens Healthineers received FDA clearance for the premium SOMATOM X.cite CT scanner. The scanner has an 82-centimeter gantry bore, which is the largest diagnostic CT bore in the industry, with applications for bariatric imaging, said Matthew Dedman, senior marketing director for the CT business at Siemens Healthineers North America.
The scanner utilizes the myExam Companion intelligent user interface concept, a tool that Dedman said acts as a GPS for the CT technologist, guiding them through how to set up and select the proper exam protocols for each patient.
“Can this patient hold their breath? Is this a screening exam? Does the patient have metal artifacts?” Dedman said. “Based on the response to these questions, the scanner will then automatically navigate through a decision tree and arrive at the proper protocol for that patient, and bring in and apply the proper scanning techniques that are appropriate for that patient. This makes the technologist more efficient and allows them to spend less time setting up exams and more time with the patient.”
This past August, the company received FDA clearance for its mobile SOMATOM On.site CT scanner
This is the first entry into the mobile CT market for Siemens Healthineers. The most common use is for head imaging in the neuro ICU, though Dedman believes there’s the potential for the technology to be used in stroke imaging.
“Without a mobile CT product, transporting the patient from the ICU to radiology requires personnel and creates an increased risk of complications, and the ICU is left understaffed,” Dedman said. “The radiology department also has to block the scanner out for up to an hour.”
The product has the same detector technology, X-ray tube technology and reconstruction software as other Siemens Healthineers CT scanners. The gantry of the system is self-shielded and lead lined, which dramatically reduces the amount of X-ray scatter, Dedman said.
“There’s only one other manufacturer in this space,” Dedman said. The current products have limitations, including degraded image quality, workflow challenges and challenges with radiation scatter in the room. We believe we’ve overcome these.”
Last September, the company’s multi-organ AI-Rad Companion Chest CT software assistant received FDA clearance for two clinical modules, Pulmonary and Cardiac. In March, it received an additional FDA clearance for its Musculoskeletal/Spine module.
At the same time, with CT playing a large role in COVID-19 diagnosis, manufacturers have responded with tailored solutions and infection control protocols designed to ensure patients are as safe as possible.
Here’s a look at the latest CT products from several manufacturers.
Canon Medical
Canon Medical Systems USA received FDA clearance in the middle of last year for its Advanced intelligent Clear-IQ Engine (AiCE), which uses deep learning reconstruction to deliver sharp, clear and distinct images, according to the company. At the time, the technology was available for Canon Medical’s Aquilion ONE / GENESIS Edition wide-area CT, and the Aquilion Precision ultra-high-definition platforms. It has since expanded access across the majority of its portfolio, including the company’s new Aquilion ONE / PRISM Edition spectral CT, FDA-cleared early this year.
“Innovation flow-down across the portfolio this quickly is unprecedented,” said Dhruv Mehta, leader of strategic development for Canon Medical.
The new Aquilion ONE / PRISM Edition also includes Deep Learning Spectral capabilities that Mehta said “help reveal spectral insights without traditional trade-offs.”
“It’s positioned to make spectral imaging routine,” Mehta said.
The company also partnered with Surfacide to offer a UV-C disinfection unit for their CT scanners that Mehta said significantly brings disinfection turnaround times down in the era of COVID-19.
In July, the company introduced a new configuration of the Aquilion ONE / GENESIS Edition wide-area CT called the Aquilion ONE / GENESIS SP for cardiovascular imaging.
“Cardiac is one of most challenging imaging exams to perform,” Mehta said. “Within a single beat of your heart, it’s able to complete an entire acquisition.”
Curvebeam
Since December of last year, Curvebeam has been working on the HiRise, a weight-bearing CT imaging system that can scan the hips and pelvis in a standing position.
“Looking at hip alignment in three dimensions could significantly influence our understanding of the anatomy and how conditions like arthritis develop,” said Vinti Singh, director of marketing for Curvebeam.
Similar to the LineUP scanner, used for the knees and lower extremities, the HiRise is small enough to fit in a doctor’s office and can plug in to a regular wall outlet, negating the need to go to the hospital for a scan.
“COVID-19 has shown us we want to rethink hospital visits,” Singh said.
The HiRise is in use for research at the University of Iowa and the company is anticipating FDA approval in the fourth quarter of this year. Last year, Curvebeam had intended to simply modify its existing LineUP to scan up to the hip, but decided to release a completely new, third-generation system.
The gantry, with a 50-centimeter bore and 40-centimeter field of view, can flip 90 degrees, so the scanner can also be used for standing upper extremity scans, as well as supine foot, ankle knee and hip scans for standing and non-weight-bearing comparisons.
The company is also in the process of developing CubeVue Autometrics, an AI platform that can automatically segment foot and ankle data sets and run measurements in a matter of minutes.
“The foot and ankle are one of the most complex regions of anatomy, with 26 bones and 28 joints,” Singh said. “It’s like a very complex puzzle. Identifying each of bones manually can take up to a day per foot.”
The company is hoping for a release of the cloud-based software by the end of the year.
FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc.
FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc. recently completed development of the latest version 1.4 for its Persona CT system software, which includes more clinical features.
The company also released FCT PixelShine, a deep learning application that improves the image quality through denoising of low-dose CT images on any scanner.
“The new release of PixelShine is designed to find the best possible noise balance for the clinician,” said Rick Banner, senior director of marketing for FUJIFILM Medical Systems U.S.A., Inc.
There are also FDA 510(k) pending updates to the company’s metal artifact reduction technology.
“Depending on the body region and type of metal, we can adjust the algorithm and make the image as beautiful and clear as possible,” Banner said.
There’s also an extended field of view, with an 85-centimeter bore and 60-plus centimeters of Hounsfield uniformity that’s FDA pending. Fujifilm believes this feature, once FDA approved and available to the market, will be crucial for oncology treatment planning.
GE Healthcare
GE Healthcare responded to the COVID-19 pandemic with a unique new solution called CT in a Box, which is a traditional scanner enclosed in a container and operated via remote control. This allows the technologist to perform the scan without entering the room. The scanner can be installed in two to three days, versus two to three weeks for a full hospital installation. It’s also easier to clean than a typical room and offers greater separation between patients and hospital staff.
The solution was developed in February, 2020 by the company’s China engineering team, with production starting in just 15 days, with the first system fully installed in Wuhan, China. The product has since been installed in more than 20 countries around the world.
“There was a desire for COVID-19 patients’ scanning to be done out of the hospital,” said Saad Sirohey, general manager for global CT digital and clinical applications for GE Healthcare.
At last year’s RSNA, GE Healthcare unveiled Revolution Maxima, part of the GE Revolution family of CT scanners. The Revolution Maxima includes a variety of applications and services designed to help simplify the CT workflow, including its new AI-based Auto Positioning solution. The solution, which generates a 3D model of the patient’s body and utilizes a deep learning algorithm to pinpoint the center of the scan range and automatically align it with the isocenter of the bore, is designed to also help avoid dose and image noise increases due to mispositioning.
At RSNA the company also displayed its Revolution EVO Gen 3, which includes TrueFidelity CT Images, GE Healthcare’s deep learning image reconstruction technology, available through the company’s Smart Subscription service.
Also through the Smart Subscription service are three new applications. The first, called Intelligent Protocoling, uses information from the patient’s exam order history and a facility’s practice to suggest the best protocol for each patient exam. The Hepatic VCAR application utilizes deep learning to automate liver and hepatic artery segmentation. And FastStroke automatically loads and processes CT studies and sends the processed images in an email format, speeding up CT stroke evaluations. The new version of FastStroke is pending FDA clearance.
Hitachi
At the end of last year, Hitachi received FDA clearance for its SCENARIA View 128-slice CT scanner.
The scanner is designed with bariatric imaging in mind, with an 80-centimeter aperture, a high-powered generator and a bariatric table that can shift left and right.
“It allows positioning to be easier and more accurate,” said Mark Silverman, director of CT Marketing for Hitachi.
The company also received FDA 510(k) clearance for Intelli IPV iterative reconstruction capability, which provides up to 83% dose reduction with the same image quality, according to Silverman.
Also new is Hitachi's SynergyDrive workflow automation, designed to reduce the number of keystrokes and clicks and allow for exam quality repeatability by automatically recognizing anatomy.
Hitachi’s new Comprehensive Ascent Program (CAP) is designed to simplify lowest cost of CT service, with one monthly payment that allows customers to lease equipment with service, X-ray tube replacement and unlimited onsite applications training included.
“We’re finding a lot of customers very interested to take advantage of that,” Silverman said.
NeuroLogica
NeuroLogica partnered with a surgical equipment manufacturer, Black Forest Medical, to create a radiolucent, carbon fiber skull clamp for interoperative use with NeuroLogica’s OmniTom CT. Previous clamps were made of metal, causing image artifacts during the CT scan, and in many cases making the CT dataset inadequate for the planned procedure.
“We are excited to partner with Black Forest Medical to bring advanced technologies, and more tightly integrated workflows to our clinical users,” said David Webster, chief operating officer of NeuroLogica.
The company also partnered with an emergency vehicle manufacturer to release an updated mobile stroke unit outfitted with an OmniTom CT scanner, which allows first responders to take immediate action in treating possible stroke patients by administering the necessary medicine or triaging them to the appropriate point of care, Webster said.
Previously, ambulances were equipped with the company’s CereTom scanner. The OmniTom provides better image quality and faster scan time, according to Webster.
Planmed
In the last 24 months, Planmed has introduced an ultra-low dose imaging capability for the Planmed Verity, a versatile cone beam CT (CBCT) imaging system that can be used in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing mode for point-of-care extremity imaging, that was released in 2012.
The technology maintains the resolution but cuts the patient dose by more than 75% as compared to the standard dose, said Steve O’Neil, North American sales manager for Planmed.
In mid-2019, the company released a new feature called CALM, a reconstruction algorithm that recognizes and corrects for minor patient movement during a scan.
Both features, the ultra-low dose imaging capability and CALM, are available as software upgrades for the company’s installed base of scanners.
Later this year, Planmed will be releasing two upgrades to the Verity platform, including an extended field of view to expand from 16 to 20 centimeters an automated stitching capability to combine up to three scans to achieve a much larger scan area than is possible with a single scan.
The company also recently signed a global distribution contract for an automated 3D analysis and treatment planning software for foot and ankle surgery from a company called Disior. The software can be used with the Verity as well as any other CBCT scanner.
Siemens Healthineers
Recently, Siemens Healthineers responded to the coronavirus pandemic by releasing its new CT Pulmonary Density AI algorithms. This workflow automation tool, which helps characterize and quantify abnormalities in the lungs of patients exhibiting COVID-19 symptoms, is part of the company’s AI-Rad Companion Chest CT software assistant.
The algorithms can be used to assess the severity and progression of COVID-19 by automatically identifying and quantifying abnormal patterns in the lungs said Peter Shen, vice president of Innovation and Digital Business at Siemens Healthineers.
“The algorithms provide several different complementary measurements, looking at ground glass opacities and consolidations, along with high-opacity abnormalities across the lung lobes that correlate to severe COVID-19 symptoms,” Shen said.
The algorithms have been trained on CT scans of COVID-specific patients from around the globe.
Just before last year’s RSNA, Siemens Healthineers received FDA clearance for the premium SOMATOM X.cite CT scanner. The scanner has an 82-centimeter gantry bore, which is the largest diagnostic CT bore in the industry, with applications for bariatric imaging, said Matthew Dedman, senior marketing director for the CT business at Siemens Healthineers North America.
The scanner utilizes the myExam Companion intelligent user interface concept, a tool that Dedman said acts as a GPS for the CT technologist, guiding them through how to set up and select the proper exam protocols for each patient.
“Can this patient hold their breath? Is this a screening exam? Does the patient have metal artifacts?” Dedman said. “Based on the response to these questions, the scanner will then automatically navigate through a decision tree and arrive at the proper protocol for that patient, and bring in and apply the proper scanning techniques that are appropriate for that patient. This makes the technologist more efficient and allows them to spend less time setting up exams and more time with the patient.”
This past August, the company received FDA clearance for its mobile SOMATOM On.site CT scanner
This is the first entry into the mobile CT market for Siemens Healthineers. The most common use is for head imaging in the neuro ICU, though Dedman believes there’s the potential for the technology to be used in stroke imaging.
“Without a mobile CT product, transporting the patient from the ICU to radiology requires personnel and creates an increased risk of complications, and the ICU is left understaffed,” Dedman said. “The radiology department also has to block the scanner out for up to an hour.”
The product has the same detector technology, X-ray tube technology and reconstruction software as other Siemens Healthineers CT scanners. The gantry of the system is self-shielded and lead lined, which dramatically reduces the amount of X-ray scatter, Dedman said.
“There’s only one other manufacturer in this space,” Dedman said. The current products have limitations, including degraded image quality, workflow challenges and challenges with radiation scatter in the room. We believe we’ve overcome these.”
Last September, the company’s multi-organ AI-Rad Companion Chest CT software assistant received FDA clearance for two clinical modules, Pulmonary and Cardiac. In March, it received an additional FDA clearance for its Musculoskeletal/Spine module.