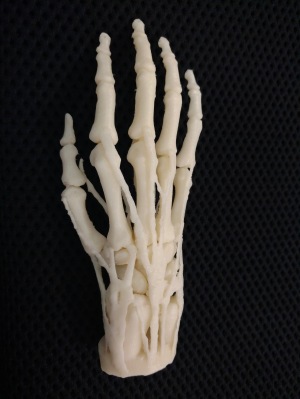
Hand mit ringen (Hand with rings).
One of the first radiographs ever
taken by Sir Wilhelm Roentgen,
depicting his wife Anna's hand,
complete with ring.
Credit: Wikipedia, public domain.
One of the first radiographs ever
taken by Sir Wilhelm Roentgen,
depicting his wife Anna's hand,
complete with ring.
Credit: Wikipedia, public domain.
Is medical 3D printing destined to become as commonplace as X-ray?
February 25, 2019
By Dr. Beth Ripley
More than 100 years ago, Mrs. Anna Roentgen saw the world’s first X-ray – taken of her left hand – and the shock of seeing the skeletal outline of her own fingers made her declare “I have seen my death”. The famous image was created by her husband, Sir Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a German mechanical engineer and physicist.
Of note, Sir Wilhelm was not focused on advancing medicine when he discovered that X-rays could see within the body. The image was just one of a series, largely consisting of inanimate objects, and there was nothing wrong with Mrs. Roentgen’s hand. However, that image captured the imagination of healthcare providers, and it’s no secret the technology has revolutionized medicine, with an estimated 3.6 billion diagnostic X-rays performed annually.
3D printing is another non-medical innovation which has captured the imagination of healthcare, and although the novel opportunity to hold your own internal organs in your hands might elicit squeamish feelings like Mrs. Roentgen’s, years from now medical 3D printing may be as commonplace as an X-ray.
3D printing was invented in the 1980’s by engineer Chuck Hull. Like Roengten, Chuck Hull’s wife was the first person to see the product of his invention – he called her out of bed in the middle of the night to come down to the lab in her pajamas, and she told him “this had better be good”. It is safe to say it was good – good enough to fuel a manufacturing technology estimated to exceed $20 billion in 2020 and impact fields as diverse as architecture, aeronautics, and medicine.
Medical 3D printing is still very much in its infancy; approximately 100 hospitals in the U.S. have in-house 3D printing capabilities today, up from three in 2010, (according to an SME 2018 Medical Additive Manufacturing / 3D Printing report). Following this trend, the Department of Veterans Health Affairs has seen growth in 3D printing hospitals from three to 20 over the past three years.
Enthusiasm for the technology and its adoption is expected to continue to grow at a rapid pace, and new medical applications are likely being imagined weekly. These include use of physically accurate models of a patient’s anatomy for pre-surgical planning, creation of bespoke implants, design of custom surgical tools and cutting guides, and custom orthotics and prosthetics, to name only a few.
Part of the magic of 3D printing is its democratization of manufacturing. Ideas can be prototyped rapidly and inexpensively, lowering the threshold for testing out new concepts and ideas. This puts the power of innovation squarely in the hands of front line staff who have the best understanding of the tough problems in healthcare that need to be solved. This explains the shift in focus of 3D printing technology from so-called “zebra” diseases (those which are rarely seen in healthcare) to common diseases that affect millions, such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and musculoskeletal disorders.
However, 3D printing isn’t as simple as dreaming up an idea and pushing a button that says print (at least not yet). Born from engineering, it requires an understanding of theoretical design principles, computer-aided design software, materials chemistry, quality assurance testing, and more. These skills are not typically taught in healthcare curricula, leaving the people with ideas and firsthand knowledge of healthcare problems often at a loss for how to translate those ideas from concept to actual product. In these early days, engineers who can speak the language of medicine and healthcare providers who can successfully communicate with engineers will play a dominant role in the medical 3D printing space. Hospitals and those in the healthcare industry who can encourage this cross-pollination of ideas and experience will see rewards in terms of new products and services that benefit patients.
Recent work by Ahmed Hosny and colleagues, published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography demonstrates this concept of cross-pollination nicely. Hosny, originally an architect by training, teamed up with two materials scientists and biologists, two radiologists, an interventional cardiologist, and a cardiac anesthesiologist to solve the tough problem of choosing the correct size heart valve replacement in cases where doctors never actually physically see the patient’s heart. This veritable Noah’s Ark of innovators each saw the problem from a different angle, and that blending of perspectives resulted in something new.
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), a groundbreaking innovation in itself, is a technique that utilizes catheters to deliver a new heart valve to a patient through their blood vessels, removing the need for open-heart surgery. This allows treatment for patients who are not surgical candidates, but it requires careful planning to ensure that the right size valve is delivered (too small or too large can lead to catastrophic results).
The physicians on the team described this sizing problem to their non-medical teammates, who borrowed from architecture and materials science to create a 3D printing solution using parametric modeling and multi-material 3D printing technology to create a biomechanical model of the patient’s diseased valve. The model allowed for testing of different replacement valve sizes in a controlled environment prior to surgery.
As a bonus, Hosny put his architectural skills to use to design a reusable 3D-printed sizing device that could replicate the TAVR heart valve for planning, overcoming a major barrier to pre-surgical valve testing (the actual valve costs thousands of dollars, making opening multiple valves for testing purposes a very costly solution).
Other promising innovations include virtual surgical planning and 3D printing of custom surgical cutting guides to decrease operating room time for mandibular surgeries (decreasing operating time by two hours can translate to roughly $9,000 in savings), creation of 3D-printed orthotic braces that are designed to withstand daily activities and enhance patient comfort, as well as 3D bioprinting of tissues that may one day address the global shortage in donor organs.
What of the fact that a large percentage of the world’s population still has no access to routine diagnostic X-ray equipment, let alone 3D printing technology? What that tells us is that our work as innovators is far from done. Increasing access to all healthcare technology, from radiographic equipment to 3D printers, is an ongoing challenge that will require creative minds across disciplines within and outside of medicine. Meanwhile, who knows what the next great technology leap will be, and whether it will change the game entirely.
About the author: Beth Ripley MD, PhD is a radiologist who specializes in translating medical imaging into virtual and 3D-printed models with the goal of changing the way doctors and patients understand and treat disease. She collaborates across multiple disciplines and has a passion for innovation and human-centered design. She is a radiologist at the VA Puget Sound Health Care System and an Assistant Professor of Radiology at University of Washington School of Medicine. She additionally serves as an Innovation Specialist for the VHA Center for Innovation and is the Chair of the VHA 3D Printing Advisory Committee.
More than 100 years ago, Mrs. Anna Roentgen saw the world’s first X-ray – taken of her left hand – and the shock of seeing the skeletal outline of her own fingers made her declare “I have seen my death”. The famous image was created by her husband, Sir Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a German mechanical engineer and physicist.
Of note, Sir Wilhelm was not focused on advancing medicine when he discovered that X-rays could see within the body. The image was just one of a series, largely consisting of inanimate objects, and there was nothing wrong with Mrs. Roentgen’s hand. However, that image captured the imagination of healthcare providers, and it’s no secret the technology has revolutionized medicine, with an estimated 3.6 billion diagnostic X-rays performed annually.
3D printing is another non-medical innovation which has captured the imagination of healthcare, and although the novel opportunity to hold your own internal organs in your hands might elicit squeamish feelings like Mrs. Roentgen’s, years from now medical 3D printing may be as commonplace as an X-ray.
3D printing was invented in the 1980’s by engineer Chuck Hull. Like Roengten, Chuck Hull’s wife was the first person to see the product of his invention – he called her out of bed in the middle of the night to come down to the lab in her pajamas, and she told him “this had better be good”. It is safe to say it was good – good enough to fuel a manufacturing technology estimated to exceed $20 billion in 2020 and impact fields as diverse as architecture, aeronautics, and medicine.
Medical 3D printing is still very much in its infancy; approximately 100 hospitals in the U.S. have in-house 3D printing capabilities today, up from three in 2010, (according to an SME 2018 Medical Additive Manufacturing / 3D Printing report). Following this trend, the Department of Veterans Health Affairs has seen growth in 3D printing hospitals from three to 20 over the past three years.
Enthusiasm for the technology and its adoption is expected to continue to grow at a rapid pace, and new medical applications are likely being imagined weekly. These include use of physically accurate models of a patient’s anatomy for pre-surgical planning, creation of bespoke implants, design of custom surgical tools and cutting guides, and custom orthotics and prosthetics, to name only a few.
Part of the magic of 3D printing is its democratization of manufacturing. Ideas can be prototyped rapidly and inexpensively, lowering the threshold for testing out new concepts and ideas. This puts the power of innovation squarely in the hands of front line staff who have the best understanding of the tough problems in healthcare that need to be solved. This explains the shift in focus of 3D printing technology from so-called “zebra” diseases (those which are rarely seen in healthcare) to common diseases that affect millions, such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and musculoskeletal disorders.
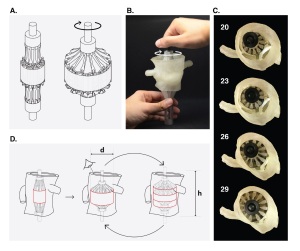
Figures from Hosny et al., JCCT 2018.
Concept drawing and actual 3D-printed sizing device,
being opened in a patient-specific 3D-printed model
of the patient’s diseased aortic valve.
Concept drawing and actual 3D-printed sizing device,
being opened in a patient-specific 3D-printed model
of the patient’s diseased aortic valve.
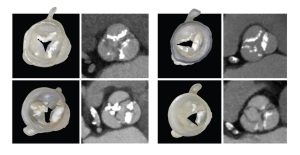
Recent work by Ahmed Hosny and colleagues, published in the Journal of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography demonstrates this concept of cross-pollination nicely. Hosny, originally an architect by training, teamed up with two materials scientists and biologists, two radiologists, an interventional cardiologist, and a cardiac anesthesiologist to solve the tough problem of choosing the correct size heart valve replacement in cases where doctors never actually physically see the patient’s heart. This veritable Noah’s Ark of innovators each saw the problem from a different angle, and that blending of perspectives resulted in something new.
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), a groundbreaking innovation in itself, is a technique that utilizes catheters to deliver a new heart valve to a patient through their blood vessels, removing the need for open-heart surgery. This allows treatment for patients who are not surgical candidates, but it requires careful planning to ensure that the right size valve is delivered (too small or too large can lead to catastrophic results).
The physicians on the team described this sizing problem to their non-medical teammates, who borrowed from architecture and materials science to create a 3D printing solution using parametric modeling and multi-material 3D printing technology to create a biomechanical model of the patient’s diseased valve. The model allowed for testing of different replacement valve sizes in a controlled environment prior to surgery.
As a bonus, Hosny put his architectural skills to use to design a reusable 3D-printed sizing device that could replicate the TAVR heart valve for planning, overcoming a major barrier to pre-surgical valve testing (the actual valve costs thousands of dollars, making opening multiple valves for testing purposes a very costly solution).
Figures from Hosny et al., JCCT 2018.
Examples of 3D-printed heart valves using parametric
leaflet modeling and multi-material 3D printing,
alongside CT images that the models were derived from.
Examples of 3D-printed heart valves using parametric
leaflet modeling and multi-material 3D printing,
alongside CT images that the models were derived from.
What of the fact that a large percentage of the world’s population still has no access to routine diagnostic X-ray equipment, let alone 3D printing technology? What that tells us is that our work as innovators is far from done. Increasing access to all healthcare technology, from radiographic equipment to 3D printers, is an ongoing challenge that will require creative minds across disciplines within and outside of medicine. Meanwhile, who knows what the next great technology leap will be, and whether it will change the game entirely.
About the author: Beth Ripley MD, PhD is a radiologist who specializes in translating medical imaging into virtual and 3D-printed models with the goal of changing the way doctors and patients understand and treat disease. She collaborates across multiple disciplines and has a passion for innovation and human-centered design. She is a radiologist at the VA Puget Sound Health Care System and an Assistant Professor of Radiology at University of Washington School of Medicine. She additionally serves as an Innovation Specialist for the VHA Center for Innovation and is the Chair of the VHA 3D Printing Advisory Committee.